Does Eating A Large Meal Before Bed Really Affect Your Sleep?
If you're not getting enough sleep at night, it can quickly begin to take a toll on your mental and physical health. According to Dr. Allison Siebern, a Head Sleep Science Advisor at Proper, "sleep deprivation has many possible side effects, including memory issues, trouble with thinking/concentration, weakened immune function, risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, and weight gain to name a few" (via Eat This, Not That!). With so much of our health depending on getting seven to nine hours of sleep per night, it's important to eliminate any factors that could prevent you from getting enough rest.
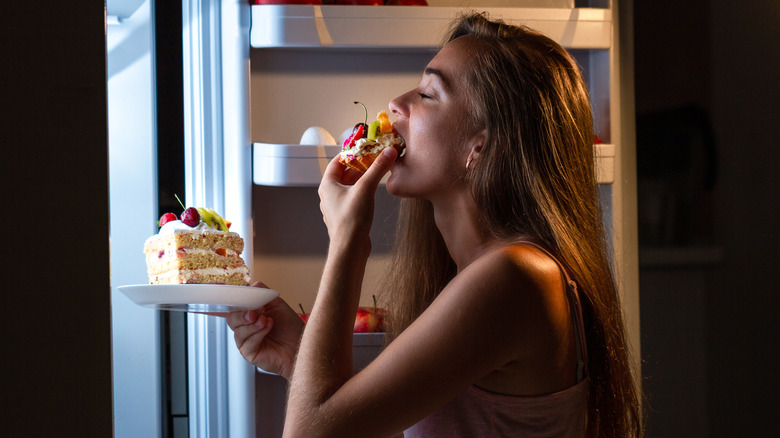
While it's hard for many of us to quiet our minds or lessen our stressors, making adjustments to our eating habits is an accessible way to increase sleep quality. Some foods, like chocolate and coffee, are obvious sleep inhibitors. But did you know that many unsuspecting meals could be contributing to your insomnia? In fact, eating anything too close to bedtime can affect your body's ability to slow down and rest.
How late-night snacks affect the body
When you have a late dinner or can't resist a midnight snack, your body has little time to digest before you hit the hay. Lying down makes it so the digestive process occurs without the help of gravity. Dr. Joseph Murray of the Mayo Clinic explains that your stomach begins producing acid after you eat and your body starts processing the food. "Now you've got a big bag of food and acid that's sitting there. You go lay down, and you no longer have gravity to keep that food and acid down. It comes up your esophagus, giving you reflux."
According to Livestrong, it's not just acid reflux that can interfere with sleep. Evidence has shown that fatty foods, and even alcohol, can have effects on sleep similar to that of caffeine. Heavy meals, or foods that are difficult to digest, cause your metabolism to run faster, sending more blood to your brain and potentially inducing vivid dreams or nightmares.
Livestrong quotes Dr. Shanna Levine, who recommends waiting at least one hour between eating and sleeping, and even more if you eat a meal high in fat. "I would allow at least three hours for meals such as this to digest. Though data is limited, it has been shown that high-fat meals prolong the time it takes you to fall into deep sleep."
Here's what to eat if you have a midnight craving
For some people, a fast metabolism can cause them to wake up starving in the morning — or even the middle of the night. If that's the case, there's no harm in eating before bed, so long as you're careful about what you eat. To make sure your sleep won't be affected, try to stick to small carb-based meals or snacks with high nutritional content, say experts quoted by The Thirty. "Usually, carbs or foods containing some carbs (think warm milk, fruit, or crackers) can help to drift you off to sleep, as the sugars hit the serotonin in the brain and can aid us to sleep," explains nutritionist Amy Shapiro (via The Thirty).
"I always suggest trying a lean protein, fresh fruit, vegetable, handful of nuts, or a serving of a whole grain," adds Summer Sanders, a holistic health coach.
While it's best to steer clear of large, fatty meals right before bed, a small snack likely won't have a negative impact on your sleep — and if you choose your snacks wisely, you'll be asleep by the time you're finished chewing.